本文将重点介绍如何通过MediatR的管道功能将FluentValidation集成到项目中实现验证功能。
什么是CQRS?
CQRS(Command Query Responsibility Segregation)也叫命令查询职责分离,是近年来非常流行的应用程序架构模式。CQRS 背后的理念是在逻辑上将应用程序的流程分成两个独立的流程,即命令或查询。
命令用于改变应用程序的状态。对应CRUD的创建、更新和删除部分。查询用于检索应用程序中的信息,对应CRUD的读取部分。
CQRS 的优缺点
优点:
- 单一职责 – 命令和查询只有一个职责。要么更改应用程序的状态,要么检索它。因此它们很容易推理和理解。
- 解耦 – 命令或查询与其处理程序完全解耦,因此在处理程序方面有很大的灵活性,可以按照自己认为最合适的方式来实现。
- 可扩展性 – CQRS 模式在如何组织数据存储方面非常灵活,为您提供了多种可扩展性选择。您可以将一个数据库用于命令和
查询。您可以使用独立的读/写数据库来提高性能,并在数据库之间使用消息传递或复制来实现同步。 - 可测试性 – 测试命令或查询处理程序非常简单,因为它们的设计非常简单,只执行一项任务。
缺点:
- 复杂性 – CQRS 是一种高级设计模式,您需要花时间才能完全理解它。它引入了很多复杂性,会给项目带来摩擦和潜在问题。在决定在项目中使用之前,请务必考虑清楚。
- 学习曲线 – 虽然 CQRS 看起来是一种简单明了的设计模式,但仍存在学习曲线。大多数开发人员习惯于用过程式(命令式)风格编写代码,而 CQRS 则与之大相径庭。
- 难以调试 – 由于命令和查询与其处理程序是分离的,因此应用程序没有自然的命令式流程。这使得它比传统应用程序更难调试。
使用 MediatR 的命令和查询
MediatR 使用接口(interface)来表示命令和查询。在我们的项目中,我们将为命令和查询创建单独的抽象。
首先,让我们看看接口是如何定义的:
using MediatR;
namespace Application.Abstractions.Messaging
{
public interface ICommand<out TResponse> : IRequest<TResponse>
{
}
}
using MediatR;
namespace Application.Abstractions.Messaging
{
public interface IQuery<out TResponse> : IRequest<TResponse>
{
}
}
我们在声明 TResponse泛型时使用了 out 关键字,这表示它是协变的。这样,我们就可以使用比泛型参数指定的类型更多的派生类型。要了解有关协变和逆变的更多信息,请查看微软文档。
此外,为了完整起见,我们需要对命令和查询处理程序进行单独的抽象。
using MediatR;
namespace Application.Abstractions.Messaging
{
public interface ICommandHandler<in TCommand, TResponse> : IRequestHandler<TCommand, TResponse>
where TCommand : ICommand<TResponse>
{
}
}
using MediatR;
namespace Application.Abstractions.Messaging
{
public interface IQueryHandler<in TQuery, TResponse> : IRequestHandler<TQuery, TResponse>
where TQuery : IQuery<TResponse>
{
}
}
这里留下一个小问题,MediatR已经提供了
IRequest和IRequest<TResponse>两个接口,那我们为什么还要再次定义IQuery<out TResponse>和ICommand<out TResponse>呢?
使用FluentValidation进行验证
FluentValidation 库允许我们轻松地为我们的类定义非常丰富的自定义验证。由于我们正在实现 CQRS,所以这里我们仅讨论对Command进行验证。由于Query对象仅仅是从应用程序获取数据,意思我们不必多此一举为Query设计验证器。
我们先设计一个 UpdateUserCommand
public sealed record UpdateUserCommand(int UserId, string FirstName, string LastName) : ICommand<Unit>;
Unit是MediatR定义的一个特殊类,表示请求不返回数据,相当于void或Task。
这个命令将用于更新已有用户(通过UserId查找)的FirstName和LastName,关于MediatR如何新增、查询和修改数据,在之前的文章中我们已经介绍过了,这里不再赘述。
接下来我们需要为 UpdateUserCommand定义一个验证器:
public sealed class UpdateUserCommandValidator : AbstractValidator<UpdateUserCommand>
{
public UpdateUserCommandValidator()
{
RuleFor(x => x.UserId).NotEmpty();
RuleFor(x => x.FirstName).NotEmpty().MaximumLength(100);
RuleFor(x => x.LastName).NotEmpty().MaximumLength(100);
}
}
此验证器将对 UpdateUserCommand的属性进行以下验证:
- UserId - 不可空
- FirstName - 不可空且最大长度不超过100个字符
- LastName - 不可空且最大长度不超过100个字符
使用 MediatR PipelineBehavior创建装饰器
CQRS 模式使用命令和查询来传达信息并接收响应。实质上是请求-响应管道。这使我们能够轻松地围绕通过管道的每个请求引入其他行为,而无需实际修改原始请求。
您可能熟悉这种名为装饰器模式的技术。使用装饰器模式的典型例子就是ASP.NET Core中间件。MediatR与中间件的概念类似,称为:IPipelineBehavior
public interface IPipelineBehavior<in TRequest, TResponse> where TRequest : notnull
{
Task<TResponse> Handle(TRequest request, CancellationToken cancellationToken, RequestHandlerDelegate<TResponse> next);
}
PipelineBehavior是请求实例的包装器,在如何实现它方面为您提供了很大的灵活性。PipelineBehavior非常适合应用程序中的横切关注点。横切关注点的很好的例子是日志记录、缓存,当然还有验证!
创建验证PipelineBehavior
为了在 CQRS 管道中实现验证,我们将使用刚才谈到的概念,即 MediatR 的 IPipelineBehavior 和 FluentValidation。
首先我们创建一个 ValidationBehavior
public sealed class ValidationBehavior<TRequest, TResponse> : IPipelineBehavior<TRequest, TResponse>
where TRequest : class, ICommand<TResponse>
{
private readonly IEnumerable<IValidator<TRequest>> _validators;
public ValidationBehavior(IEnumerable<IValidator<TRequest>> validators) => _validators = validators;
public async Task<TResponse> Handle(TRequest request, CancellationToken cancellationToken, RequestHandlerDelegate<TResponse> next)
{
if (!_validators.Any())
{
return await next();
}
var context = new ValidationContext<TRequest>(request);
var errorsDictionary = _validators
.Select(x => x.Validate(context))
.SelectMany(x => x.Errors)
.Where(x => x != null)
.GroupBy(
x => x.PropertyName,
x => x.ErrorMessage,
(propertyName, errorMessages) => new
{
Key = propertyName,
Values = errorMessages.Distinct().ToArray()
})
.ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Values);
if (errorsDictionary.Any())
{
throw new ValidationException(errorsDictionary);
}
return await next();
}
}
处理验证异常
为了处理遇到验证错误时抛出的 ValidationException,我们可以使用 ASP.NET Core的 IMiddleware接口。
internal sealed class ExceptionHandlingMiddleware : IMiddleware
{
private readonly ILogger<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware> _logger;
public ExceptionHandlingMiddleware(ILogger<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware> logger) => _logger = logger;
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next)
{
try
{
await next(context);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
_logger.LogError(e, e.Message);
await HandleExceptionAsync(context, e);
}
}
private static async Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext httpContext, Exception exception)
{
var statusCode = GetStatusCode(exception);
var response = new
{
title = GetTitle(exception),
status = statusCode,
detail = exception.Message,
errors = GetErrors(exception)
};
httpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
httpContext.Response.StatusCode = statusCode;
await httpContext.Response.WriteAsync(JsonSerializer.Serialize(response));
}
private static int GetStatusCode(Exception exception) =>
exception switch
{
BadRequestException => StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest,
NotFoundException => StatusCodes.Status404NotFound,
ValidationException => StatusCodes.Status422UnprocessableEnttity,
_ => StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError
};
private static string GetTitle(Exception exception) =>
exception switch
{
ApplicationException applicationException => applicationException.Title,
_ => "Server Error"
};
private static IReadOnlyDictionary<string, string[]> GetErrors(Exception exception)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, string[]> errors = null;
if (exception is ValidationException validationException)
{
errors = validationException.ErrorsDictionary;
}
return errors;
}
}
设置依赖注入
在运行应用程序之前,我们需要确保已向 DI 容器注册了所有服务。MediatR的DI注入方式之前已经介绍过,这里主要演示FluentValidation的注入。由于 ValidationBehavior依赖 IValidator<T>,因此需要注入我们定义的Validator。
// 在Startup.cs中配置
services.AddValidatorsFromAssembly(typeof(Application.AssemblyReference).Assembly);
// 在Program.cs中配置(≥ net 6.0)
builder.Services.AddValidatorsFromAssembly(typeof(Application.AssemblyReference).Assembly);
最后我们需要将 ExceptionHandlingMiddleware也注册到DI容器和ASP.NET Core的管道中:
// 在Startup.cs中配置
services.AddTransient<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware>();
// 在Program.cs中配置(≥ net 6.0)
builder.Services.AddTransient<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware>();
app.UseMiddleware<ExceptionHandlingMiddleware>();
测试验证管道
在项目的Controllers文件夹中找到UserController:
/// <summary>
/// The users controller.
/// </summary>
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public sealed class UsersController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ISender _sender;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="UsersController"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
public UsersController(ISender sender) => _sender = sender;
/// <summary>
/// Updates the user with the specified identifier based on the specified request, if it exists.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="userId">The user identifier.</param>
/// <param name="request">The update user request.</param>
/// <param name="cancellationToken">The cancellation token.</param>
/// <returns>No content.</returns>
[HttpPut("{userId:int}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> UpdateUser(int userId, [FromBody] UpdateUserRequest request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var command = request.Adapt<UpdateUserCommand>() with
{
UserId = userId
};
await _sender.Send(command, cancellationToken);
return NoContent();
}
}
我们可以看到,UpdateUser 操作非常简单,它从路由中获取用户Id,从请求正文中获取FirstName和LastName,然后创建一个新的 UpdateUserCommand实例并且通过管道发送命令。最后返回204(请求成功但无响应内容)状态码。
接下来我们通过Swagger调用API接口:
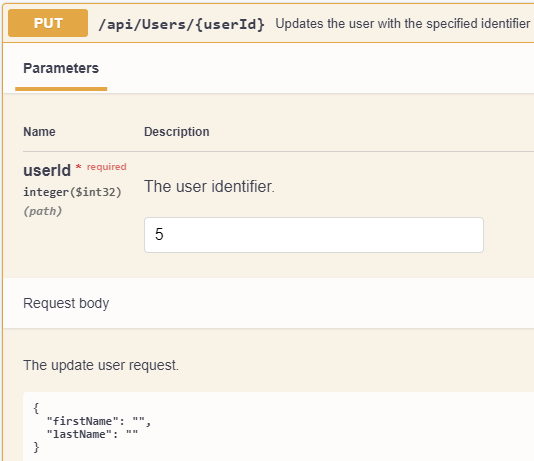
可以看到,请求的FirstName和LastName都是空白字符串。
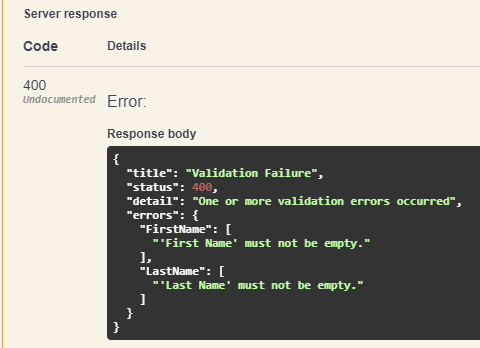
补充内容之后再次发送请求。
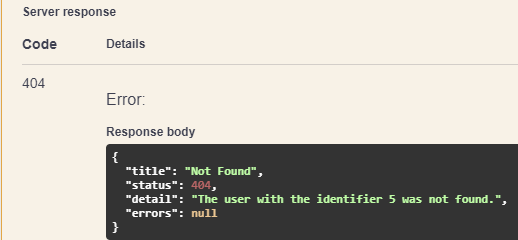
结论
在本文中,我们介绍了CQRS 模式的一些更高级的概念,以及如何在应用程序中通过横切的方式实现数据验证,同时也简单的介绍了如何通过ASP.NTE Core的中间件实现全局异常处理。
点关注,不迷路。
如果您喜欢这篇文章,请不要忘记点赞、关注、转发,谢谢!如果您有任何高见,欢迎在评论区留言讨论……

